Two of the most well-known cloud computing systems are Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. The debate over which of these top providers is better is ongoing, and the ultimate decision depends on your company’s requirements and needs. AWS offers a greater variety of services and seems more dependable because it has been on the market for a longer period of time, while Azure is more suited to Windows users thanks to its compatibility.
Let’s first get an in-depth understanding of cloud platforms to better differentiate these two cloud providers, finding which one better suits your business needs.
What is the Cloud?
The cloud refers to a server that can be remotely accessed through the Internet. You can find cloud servers in data centers. Companies and users can avoid managing physical servers and run software applications on their own computers by implementing cloud computing. The latter refers to a technology that uses the internet to store and manage data on remote servers and then provides internet-based data access. It’s about delivering hosted services (e.g. servers, networking, data storage, software) through the Internet to provide flexible resources.
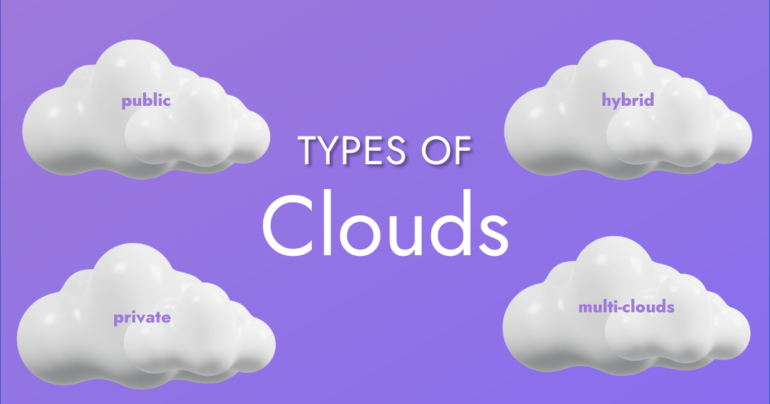
We can identify four different types of Clouds:
- Public Cloud — Public cloud platforms (e.g. Microsoft Azure, AWS, Alibaba, Google Cloud Platform, etc.) that deliver resources through the Internet. They are run by third parties who offer cloud services to the general public over the internet with pay-as-you-go billing options. Multitenancy is one of the fundamental characteristics of public clouds. It’s designed to serve multiple users instead of a particular one.
- Private Cloud — A single organization is the only user of a private cloud platform. It is typically hosted by a third-party service provider or at an on-site data center. Every cloud turns into a private cloud when the underlying IT infrastructure is given to a single client with totally isolated access.
- Hybrid Cloud — If we combine private and public clouds, we can have a hybrid cloud. A company may use the public cloud as a backup for its private cloud or use the public cloud for one service and the private one for another service. A hybrid cloud combines the facilities of public and private clouds.
- Multi-clouds — This refers to using multiple public clouds. A company using many clouds rents virtual servers and services from various outside providers. Although not all multi-clouds are hybrid clouds, all hybrid clouds are multi-clouds. When multiple clouds are linked together by some kind of integration or orchestration, they become hybrid clouds.
Digi-tip: A public cloud may be more suitable for workloads with large volumes or changing demands.
What is a Cloud Platform?
In an Internet-based data center, the term ‘cloud platform’ refers to the hardware and operating system of a server. It makes it possible for hardware and software products to coexist remotely and on a large scale. Through cloud platforms, developers can run apps and write codes. It is built by cloud service providers who need to have extra levels of development to incorporate technologies, such as application programming interfaces (APIs), security, orchestration, etc.
Cloud computing services include the software, platforms, infrastructure, or technologies that users can access via the Internet without any need to download software.

What Are Cloud Services?
Users who use cloud services can store documents and software on remote servers and then access the entire database online. Cloud service includes platforms, software, and infrastructure that is hosted by a third-party provider and users can access them via the Internet. The development of cloud-native apps and the adaptability of working in the cloud are promoted by cloud services. Users only need an Internet connection, computer, and an operating system to use cloud services.
Azure vs. AWS Features
Ensuring to choose the right cloud service provider is essential for your long-term success. Making a decision could be difficult since there are numerous cloud service providers that offer a wide range of services. So, how to choose a cloud service provider? Since AWS and Azure are the top two cloud service providers, we’ll talk about both of them to compare their features and determine which is the best option.
The main features and cloud capabilities offered by Microsoft’s Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are similar. You must analyze several aspects, including rates of data availability, cloud storage costs, and data transfer loss rates to choose the best cloud service provider.
AWS and Azure provide the same fundamental features with regard to storage, databases, and networking. The survey done by Synergy Research Group shows that Amazon maintains its top spot as the market leader, with its 33% global market share followed by Microsoft at 22%, and Google at 10%.
Let’s dive deeper into the two most popular cloud providers:
- AWS — an Amazon subsidiary, provides more than 200 services from global data centers and is used by many users, including large enterprises, startups, leading government agencies, etc. It offers its customers APIs and on-demand cloud computing services. It was established in 2002 and previously solely offered web-based services, but in 2006, it added cloud computing to its offerings. Because of this, it has an edge over Azure in the market, since it was the first service provider for cloud computing. It’s a platform that offers users and clients access to database storage, computing power, content distribution, and other features. It is designed to assist programmers in creating complex applications that are scalable, dependable, and flexible. This platform provides solutions to many industries thanks to its global network, which spans 81 availability zones in 25 different regions around the world. It also offers more than 200 products to help companies with their IT needs.
- While Microsoft Azure helps to manage applications via Microsoft-operated data centers and provides many cloud services, such as storage, computing, networking, etc. It is designed specifically to support the development, testing, deployment, and management of applications and services, by providing on-premises, multi-cloud and hybrid solutions. Thanks to its provisions, you can take on problems using any infrastructure, framework, or programming language. It offers over 200 different products to meet the demands of your company. The fact that many businesses use Windows is one of Azure’s most competitive advantages. And Microsoft has put a lot of effort into making its hybrid computing solutions available, which will benefit businesses that require hybrid environments.
These two have many similarities in core features but differ in other aspects.
AWS vs. Azure Performance Comparison
Now let’s take a look at some key differences to compare the performance of these two cloud platforms:
- Computing Power: There are two options for businesses looking for quick data analysis or graphics processing — either to upgrade hardware or move to the cloud. Public cloud services aim to achieve this and the main computing option provided by AWS is elastic cloud computing (EC2), which can be customized for different applications and offer flexible computing on demand. Other services for app deployment include AWS Lambda, Elastic Beanstalk, EC2 container service, and Autoscaling. EC2 users can create their virtual machines (VMs), choose or change machine images (MIs), alter the size, power, and memory of the VMs as needed, and decide how many VMs they require. While Azure’s compute services are based on VMs and have many other tools to help to create cloud-based applications.
- Networking and Content Delivery: Network performance is crucial in cloud solutions, and cloud users pay special attention to safe and isolated networks. By using AWS’ Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), users can create separate networks within the cloud. A user can create subnets, route tables, network gateways, and private IP address ranges inside a VPC. While with Azure, you can build isolated networks by using a Virtual Network (VNET) instead of a VPC. For extending on-premise data centers into the cloud without harming data or business processes, both AWS and Microsoft Azure provide cloud-compatible firewall solutions.
- Storage: The way cloud service providers store data is essential. AWS’ storage services are the oldest ones, but Azure’s storage options are also dependable. Both AWS and Azure are powerful in storage capabilities and offer all the fundamental features. AWS’ storage system is referred to as Storage Service (S3), while Microsoft Azure’s is Blob storage. Customers may benefit from a scalable, secure, and reliable storage solution with AWS S3 for use cases involving both unstructured and structured data. Azure, on the other hand, provides data storage through Azure Queues, Azure Blogs, Azure Tables, Azure Files, and Azure Disks. Object size limits of AWS are 5 TB and of Azure 4.75 TB.
- Pricing: AWS and Azure both have affordable prices and a pay-as-you-go pricing structure. Both AWS and Azure provide free trial tiers with constrained use restrictions so that users can test out their services before deciding to purchase them. Azure costs more per GB than AWS. Pay-as-you-go billing offered by AWS can be changed at any time without paying any fees or giving prior notification. For access to resources that are billed at monthly rates upfront, Azure requires that every customer has contracts in place beforehand. While Azure charges per minute, AWS’s pay-as-you-go approach is billed on an hourly basis. Though, with Azure, you can make short-term commitments and select between prepaid or monthly fees. On Azure, shorter-term subscription plans offer more flexibility.
- Databases: Today, all software programs need databases to store data. Whether you require a relational database or a NoSQL solution, Azure and AWS both offer database services. The SQL Server database from Microsoft and Amazon’s RDS (Relational Database Service) is durable and available and offers automated replication. What about SQL server on AWS vs Azure? While Azure’s SQL database service is entirely based on MS SQL Server, Amazon’s RDS offers six prominent database engines. You can do different DB operations through Azure’s tooling and interface, while AWS has more instance kinds that you may offer and can get extra control over DB instances.
- Machine Learning: SageMaker on AWS offers complete freedom and flexibility for building ML models. SageMaker is perfect for developers with coding knowledge, experience, and data engineering expertise since SageMaker requires users to be an expert in Python and Jupiter Notebook to employ AWS capabilities. In contrast, the main goal of Azure ML Studio is to offer a coding-free experience, using drag-and-drop components. One does not need to be an expert in complex data science techniques or know Python. The service is intended for data analysts that choose a straightforward user interface and a visual presentation of the elements.

Azure Security vs. AWS Security
How to evaluate cloud service provider security correctly? AWS chooses secure settings and options by default, providing increased privacy. While Azure uses Microsoft’s Cloud Defender service, which uses artificial intelligence to prevent potential risks for security and data privacy. Though, you need to know that it cannot be completely safe by default. Azure’s strength is the security framework that you can manage from a single directory.
Digi-Tip: Examine your business requirements before selecting a cloud provider.
To conclude, thanks to its size and wide range of services, as well as its long business history, AWS seems better. However, while it is better suited for large-scale businesses, Microsoft Azure is preferable for businesses that need a hybrid environment and use Microsoft.
If you have any other questions or look for high-quality web development services, don’t hesitate to contact Digilite’s experienced tech team.